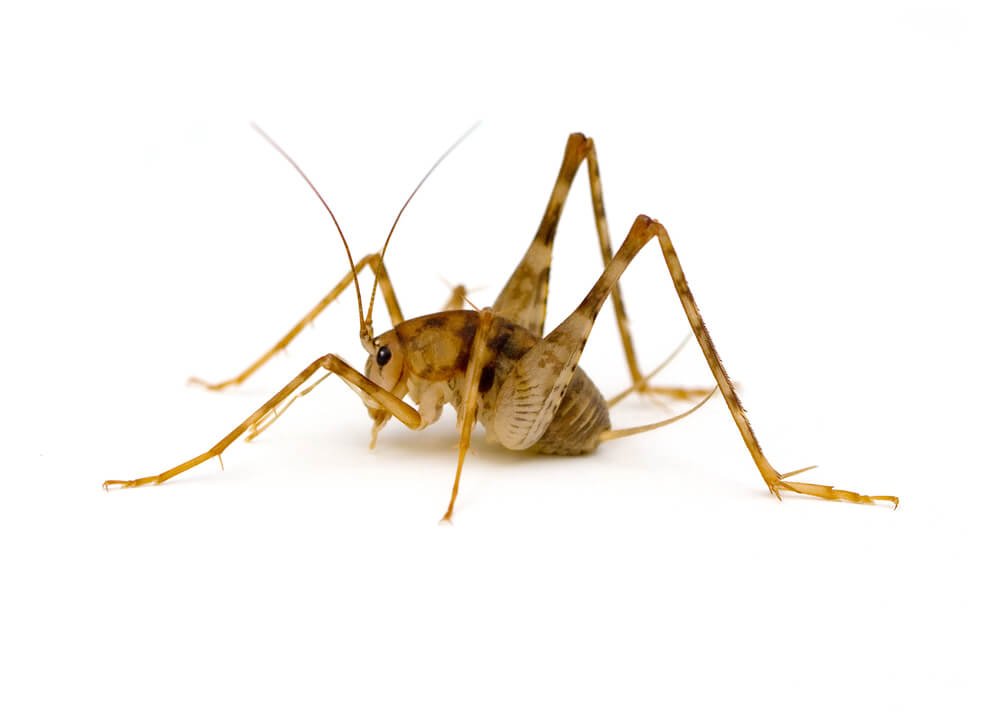
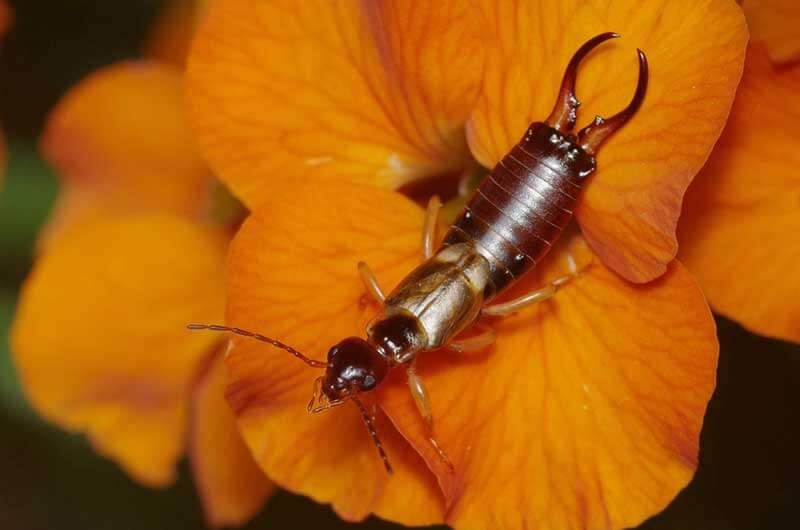
What are Earwigs?
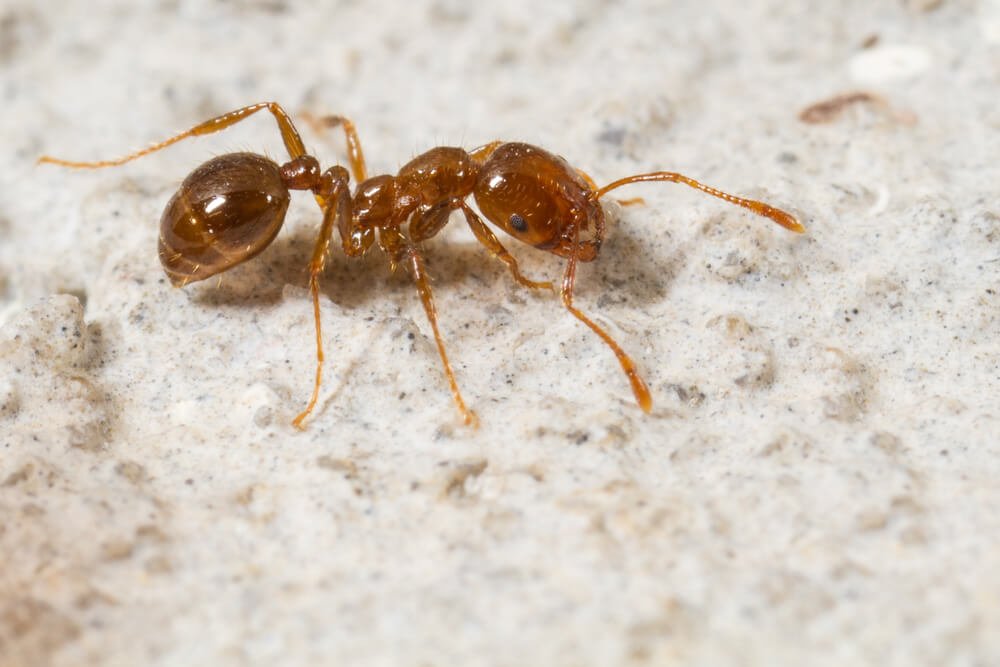
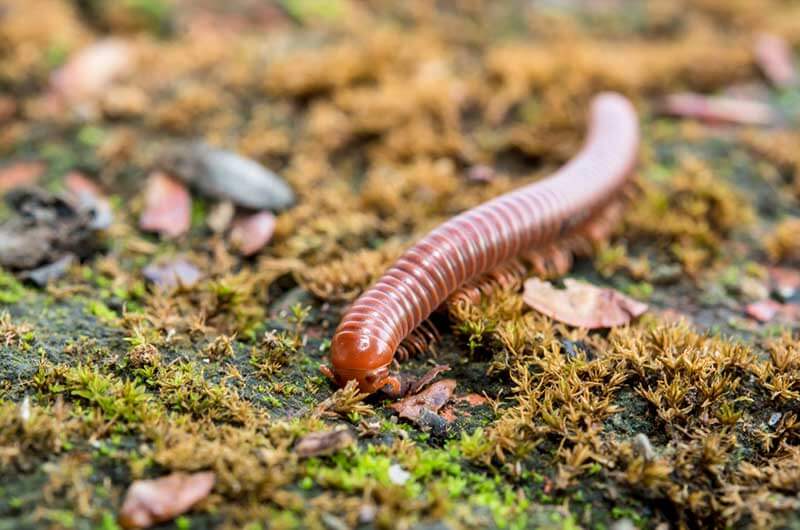
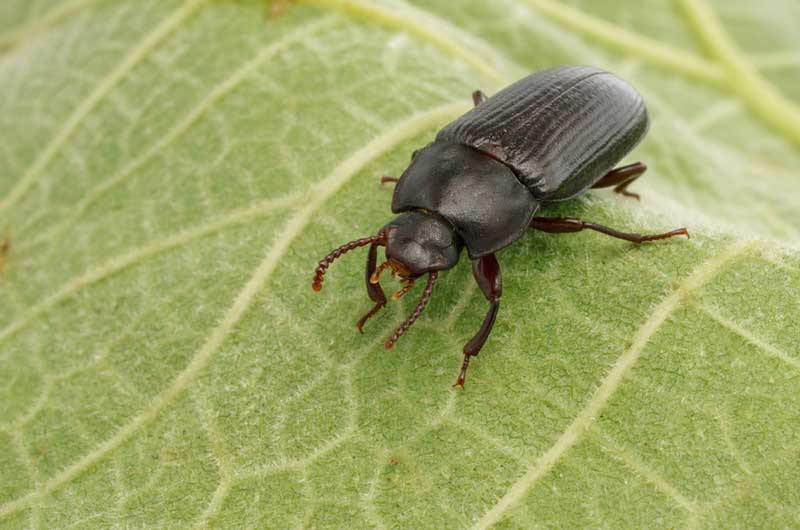
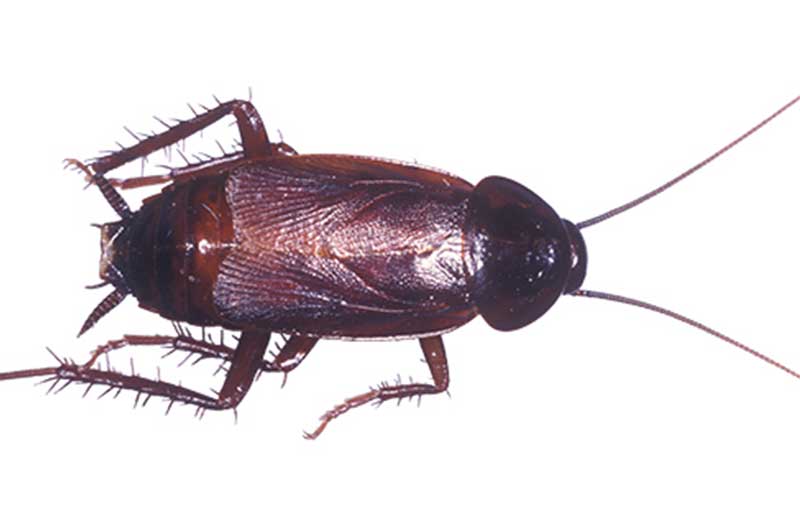
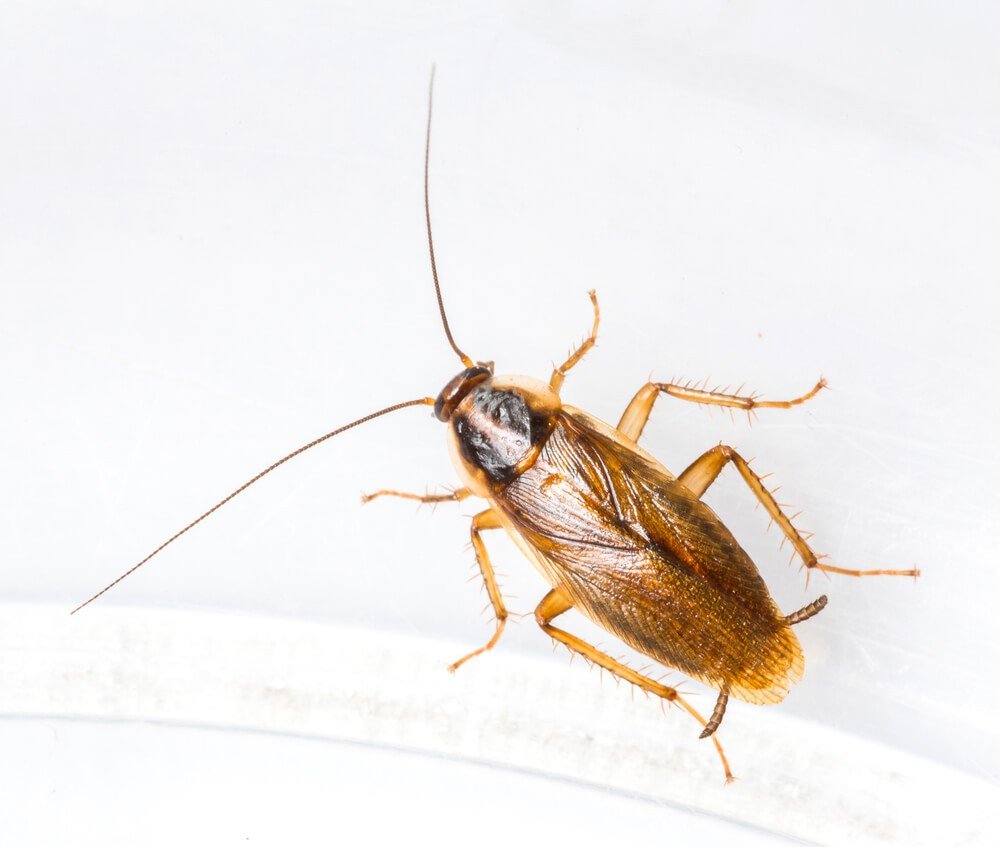
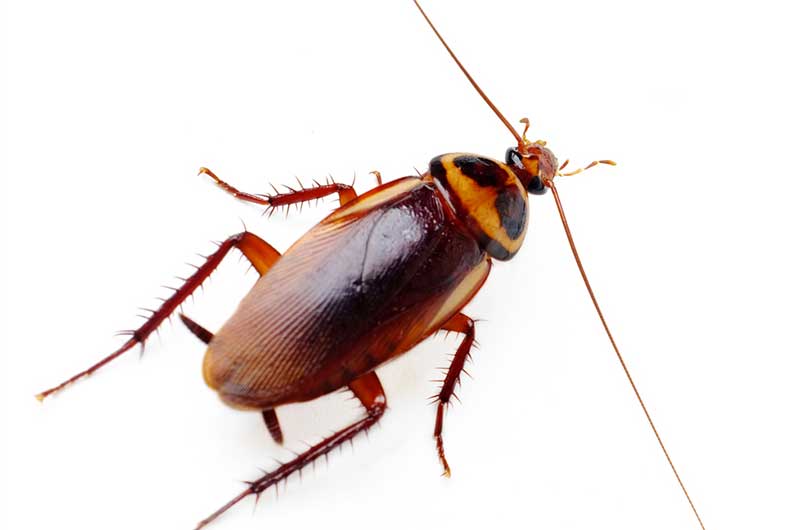
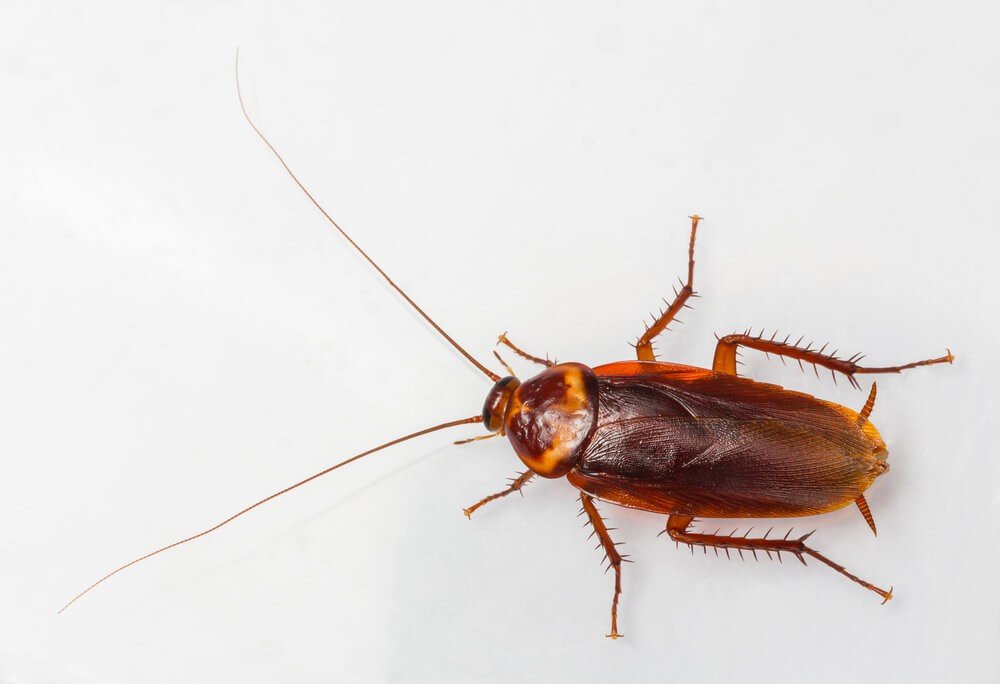
 Earwigs are one-inch long dark brown insects that are easily identified by their pincers. They use these pincers for defense and for sparing with rival earwigs. Depending on the species, adults range in size from 5-25 mm. They are slender insects with two pair of wings. Some species produce a foul smelling liquid that they use for defense.
Earwigs are one-inch long dark brown insects that are easily identified by their pincers. They use these pincers for defense and for sparing with rival earwigs. Depending on the species, adults range in size from 5-25 mm. They are slender insects with two pair of wings. Some species produce a foul smelling liquid that they use for defense.
Earwigs are outdoor pests that occasionally find their way indoors. They enter homes by crawling inside through cracks, gaps and holes that lead inside the structure. These common entry points include gaps around poorly sealed doors and windows; through crevices and gaps in the areas where foundations meet siding; through unscreened attic and foundation vents; and through access doors leading into crawl spaces.
They cannot survive long indoors unless it is very damp. While taking up residence in your home the earwigs feed on food scraps, live or dead insects, mold or house plants. Prime indoor hiding places are cracks and crevices near kitchen, bathroom, and laundry room sinks or in house plants and stacks of damp newspaper.
Not only are they quick movers, they are also nocturnal, and tend to hide out during the day. They like decaying wood and plant material, and dark, damp spaces. Often times they can be found in basements and woodpiles.
Generally, Earwigs are not much of a threat, they are just a big annoyance!
Here are some tips to prevent earwigs from entering your home:
-
Look for ways to eliminate damp moist conditions particularly around crawl spaces, faucets, and along the foundations.
-
Rain gutters and spouts should direct water away from the house foundation.
-
Caulk or use weather stripping at all possible entry points such as doors, windows, pipes and other entry points at the ground level.
-
Change landscaping by creating a clean, dry border immediately around the foundation wall. Gravel or ornamental stones can make an attractive barrier against earwigs and other pest invaders.